Kinetic analysis for oxidation and anti-oxidation of biomembrane lipids
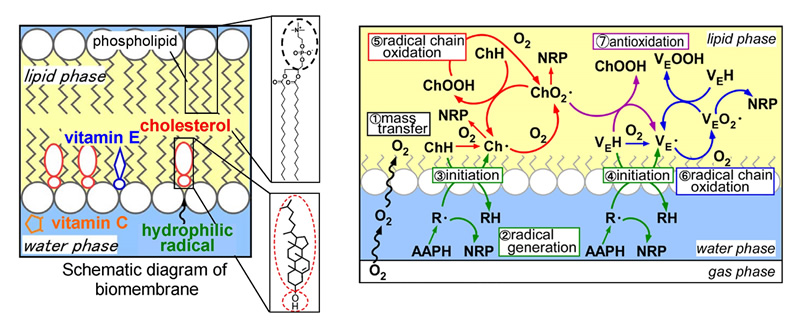
Oxidation of the biomembrane lipids which comprise the cells of internal organ tissues of human beings is known to be a cause of lifestyle-related diseases such as cancer and arteriosclerosis. As shown in the diagram, a biomembrane is a dual membrane comprised primarily of phospholipids and cholesterol, and it is thought that water soluble radicals present in the surrounding aqueous phase (blood) cause oxidation of biomembrane lipids such as phospholipids and cholesterol. On the other hand, it is said that if antioxidants such as water soluble vitamin C and lipid soluble vitamin E are ingested orally, they are transported via the blood. Then, depending on polarity, the water soluble type is kept in the blood, and the lipid soluble type is kept in the biomembranes, and they both suppress biomembrane lipid oxidation due to water soluble radicals. Oxidation of biomembranes progresses, through the course of oxidation and antioxidation reactions, as biomembrane lipids, water soluble radicals, and water/lipid soluble antioxidants interact in a complex fashion. Therefore, the reaction mechanism must be elucidated in detail in order to effectively prevent oxidation.
In this research, we are conducting oxidation experiments on biomembrane lipids such as phospholipids and cholesterol using ribosomes with a structure similar to biomembranes, and thereby working to elucidate the oxidation/antioxidation mechanisms due to water/lipid soluble antioxidants. In particular, we aim to simulate actual in vivo lipid oxidation activity by developing kinetic models which take into account the interphase mass transfer and reaction mechanism of each component.
|


